This sum is typically displayed at the bottom of the corresponding side of the account. This simple structure provides a clear and immediate way to track increases and decreases in a specific financial account, such as cash, accounts payable, or sales revenue. T accounts are categorized into assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses, reflecting the elements of the accounting equation.
#1 – General Ledger
The difference between the current balance and the needed ending balance is the amount for the adjusting entry. Here is an example of two T-accounts posting the purchase of a car. As you can see, the cash account is credited for the purchase of the car and the vehicles account is debited. Although double-entry accounting has some drawbacks, it is indispensable for most businesses because it produces comprehensive financial statements. These statements allow for historical financial comparisons, help manage expenses efficiently, and assist in future strategic decision-making. This entry ensures the accounting T-account equation remains balanced by recording the cash collection and reducing the receivable.
Entrepreneurs and Small Business Owners
In a double-entry system, for every transaction, the total amount debited must equal the total amount credited. For example, if a company purchases an asset like inventory, it would debit the asset account and credit the cash or accounts payable account, reflecting the exchange. T-accounts facilitate this process by t account definition providing a clear, visual representation of both sides of the transaction. A single-entry accounting system records each financial transaction only once, which does not provide enough detail for the T-account’s visual format. In contrast, a double-entry system records every transaction twice—once as a debit and once as a credit—allowing T-accounts to separate and display these entries. This makes T-accounts an effective tool for businesses using double-entry accounting to track and distinguish debits and credits accurately.

Connecting T-Accounts to Financial Statements
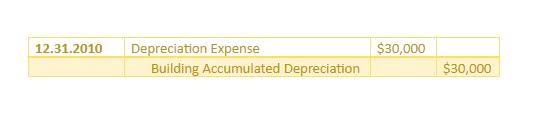
The total difference between the debit and credit columns will be displayed on the bottom of the corresponding side. In other words, an account with a credit balance will have a total on the bottom of the right side of the account. Expense T accounts document costs incurred to generate revenue, such as cost of goods sold (COGS), salaries, and rent. These accounts follow the matching principle, which aligns expenses with related revenue within the same period. For example, when a company pays $2,000 in rent, the rent expense account is debited, and the cash account is credited to reflect the outflow.
- One of the fundamental principles of financial accounting is the T account.
- Learn how small businesses can handle bookkeeping effectively and scale faster with clean books.
- T-accounts help keep the books balanced by showing all payables and payments clearly.
- T accounts are one of the primary forms of performing double-entry accounting.
- Likewise, create T-accounts for different expense categories like rent, utilities, or charitable donations.
- T accounts are central to the double-entry accounting system, and they show how transactions affect accounts like cash, accounts receivable, and revenue.
T-Account vs Trial Balance
Total debits amount to $320,000 while total credits amount to $230,000. This double-entry T-account example ensures the accounting equation stays balanced, with total debits equal to total credits. T-accounts, or say, ledger accounts, are the accounts that are used to post the balancing amounts to the financial accounts. These accounts follow the double-entry system, which means the impact of the transaction will be https://linhkienviendong.com/normal-balance-debit-and-credit/ effective on two different accounts. And the representation becomes easier with two different sides, called the debit and credit.
- Tools like bank reconciliation statements or automated accounting software streamline this task.
- Debits are entered into the left hand side of a t-account whereas credits into the right hand side.
- The asset Equipment increases by $2,500 and is recorded as a debit.
- The left side is consistently designated for “debit” entries, while the right side is always used for “credit” entries, regardless of the account type.
- So, when you borrow money from the bank (debiting cash, which is an asset), you’re also increasing your liabilities (debit).
- This prepaid £6,000 represents an asset because the landlord owes the business 3 months usage of their property rent has been paid in advance.
- T accounts perfectly demonstrate this double-entry accounting system.
What is an Accounting Method?

Metals and Co. has sold iron worth $50,000 to their customer named Factory Innovators on $30,000 cash and remaining on a credit basis. Keep a look at the below-mentioned information to further understand what the T-account looks like.
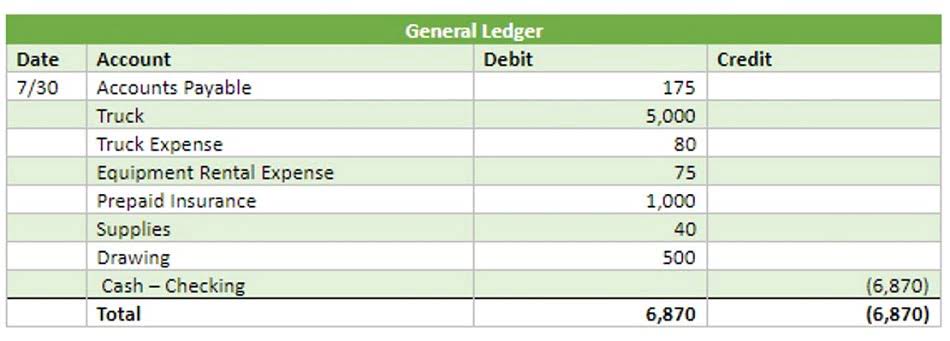
What are some common examples of T accounts?
Each type tracks specific financial activities, ensuring accurate Travel Agency Accounting reporting in financial statements. Transactions are then recorded on the left (debit) or right (credit) side of the T, reflecting increases or decreases in that element. This visual representation helps them ensure their records’ accuracy and easily prepare financial statements. For instance, consider a service-based business that recognizes revenue when services are rendered, regardless of whether payment is received immediately.
